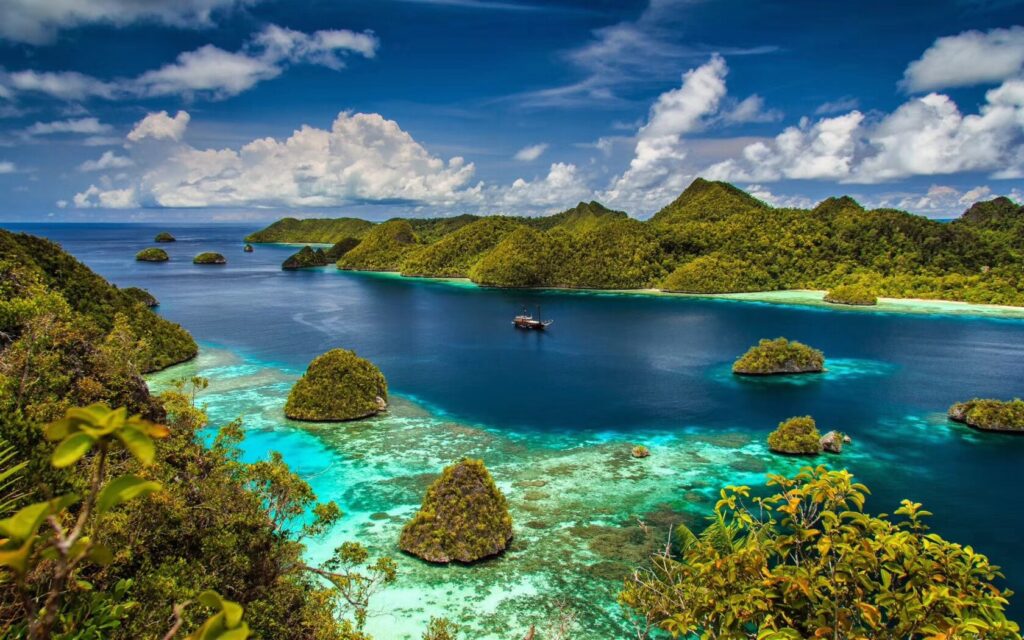
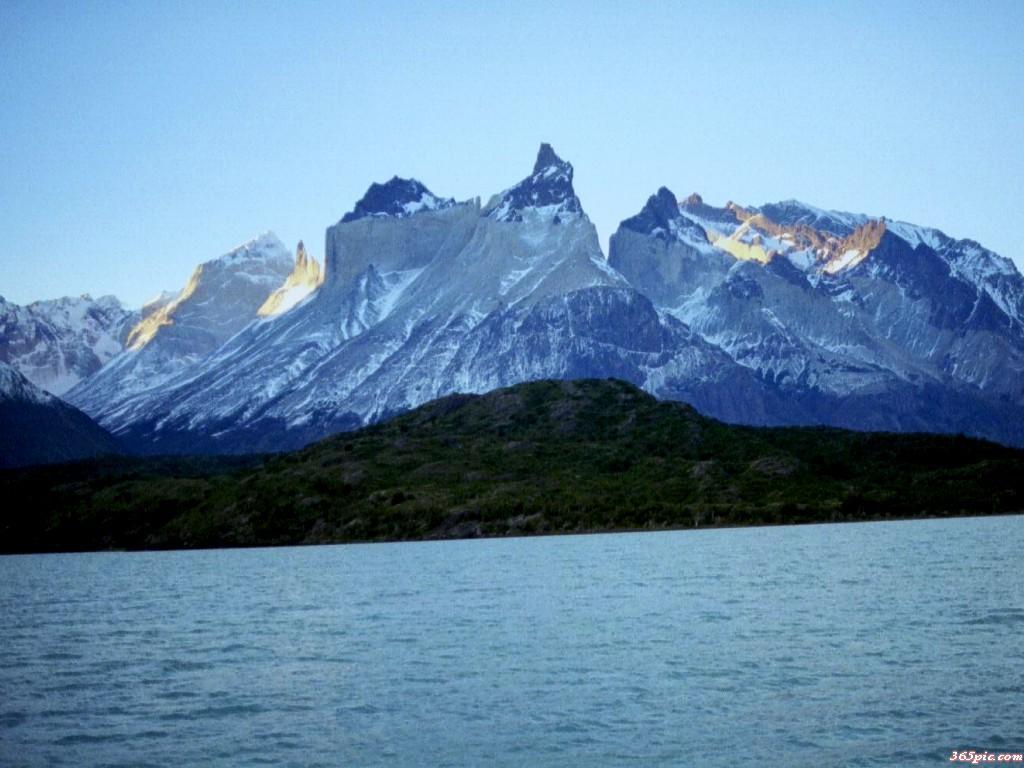
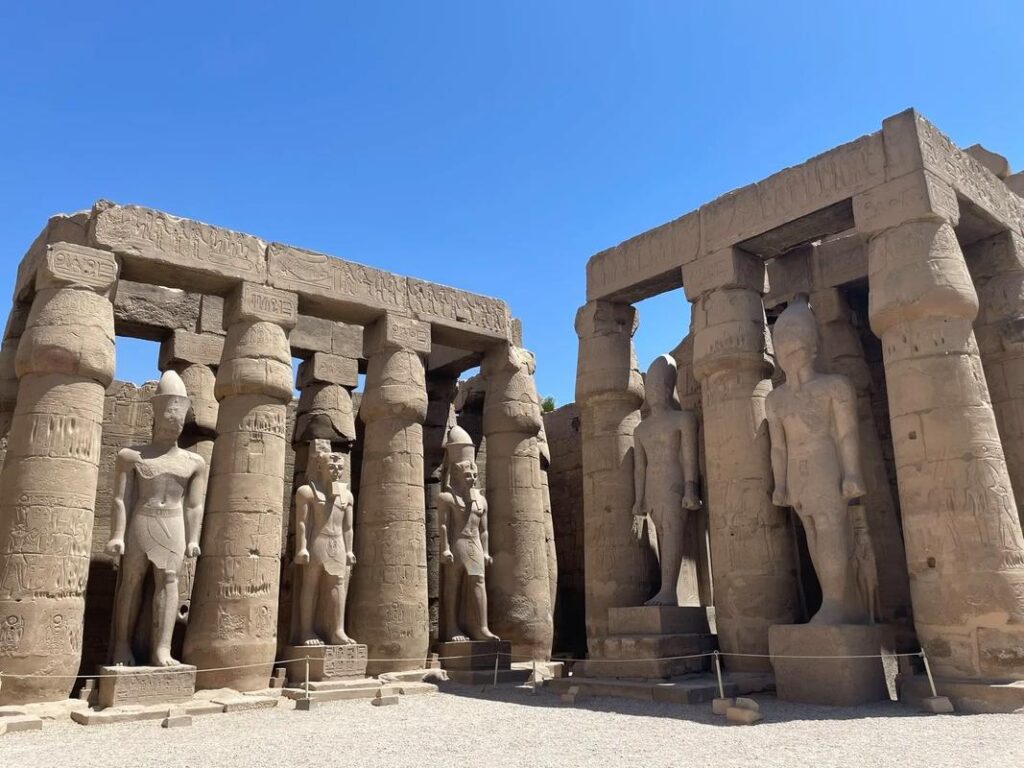
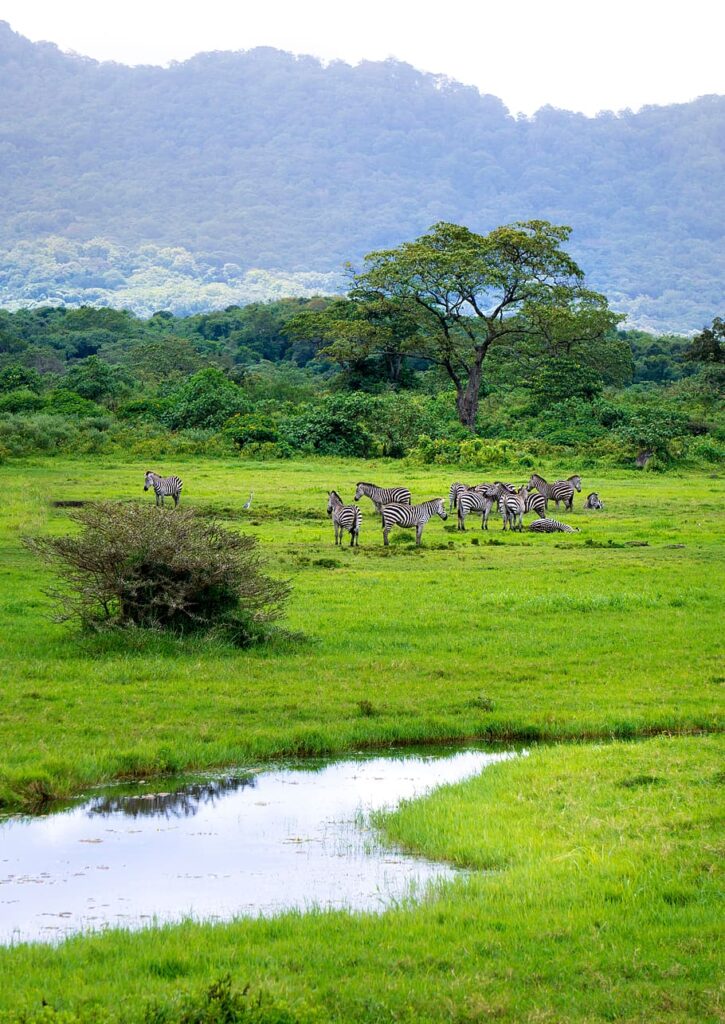
The Middle East is a historical and political region of Africa-Eurasia with no clear definition. The term “Middle East” was popularized around 1900 by the British, and has been criticized for its loose definition. The Middle East traditionally includes countries or regions in Southwest Asia and parts of North Africa. The corresponding adjective to Middle East is Middle-Eastern and the derived noun is Middle-Easterner. The history of the Middle East dates back to ancient times, and throughout its history the Middle East has been a major center of world affairs. The Middle East generally has an arid and hot climate, with several major rivers providing for irrigation to support agriculture in limited areas. Many countries located around the Persian Gulf have large quantities of crude oil. In modern times, the Middle East remains a strategically, economically, politically, culturally, and religiously sensitive region. Etymology The term “Middle East” may have originated in the 1850s in the British India Office,[1] and became more widely known when American naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan used the term.[2] During this time the British and Russian Empires were vying for influence in Central Asia, a rivalry which would become known as The Great Game. Mahan realized not only the strategic importance of the region, but also of its center, the Persian Gulf.[3][4] He labeled the area surrounding the Persian Gulf as the Middle East, and said that after the Suez Canal, it was the most important passage for Britain to control in order to keep the Russians from advancing towards India.[5] Mahan first used the term in his article “The Persian Gulf and International Relations”, published in September 1902 in the National Review, a British journal. The Middle East, if I may adopt a term which I have not seen, will some day need its Malta, as well as its Gibraltar; it does not follow that either will be in the Persian Gulf. Naval force has the quality of mobility which carries with it the privilege of temporary absences; but it needs to find on every scene of operation established bases of refit, of supply, and in case of disaster, of security. The British Navy should have the facility to concentrate in force if occasion arise, about Aden, India, and the Persian Gulf.[6] Alfred Thayer MahanMahan’s article was reprinted in The Times and followed in October by a 20 article series entitled “The Middle Eastern Question”, written by Sir Ignatius Valentine Chirol. During this series, Chirol expanded the definition of the “Middle East” to include “those regions of Asia which extend to the borders of India or command the approaches to India.”[7] With the series end in 1903, The Times removed quotation marks from subsequent uses of the term.[8] Until World War II, it was customary to refer to areas centered around Turkey and the eastern shore of the Mediterranean as the Near East, while the Far East centered on China.[9] The Middle East then meant the area from Mesopotamia to Burma, namely the area between the Near East and the Far East. The sense described in this article evolved during the war, perhaps influenced by the ancient idea of the Mediterranean as the “sea in the middle”. One widely used definition of the “Middle East” is that of the airline industry, maintained by the IATA standards organization. This definition — as of early 2007 — includes Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Palestinian territories, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syrian Arab Republic, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.[10] This definition is used in world-wide airfare and tax calculations for passengers and cargo. Criticism and usage Many have criticized the term Middle East for what they see as Eurocentrism,[11][12] because it was originally used by Europeans (although Alfred Mahan was American) and reflects the geographical position of the region from a European perspective. It is also criticized due to the fact that the term today is often used to only refer to the Arab world, making the situation more confused. Today the term is used by Europeans and non-Europeans alike, unlike the similar term Mashreq, used exclusively in Arabic-language contexts. The region is only east from the perspective of Europe. To an Indian, it lies to the west; to a Russian, it lies to the south. The description Middle has also led to some confusion over changing definitions. Before the First World War, Near East was used in English to refer to the Balkans and the Ottoman Empire, while Middle East referred to Persia, Kurdistan, Afghanistan, present day Pakistan and Central Asia, Turkistan and the Caucasus. In contrast, Far East refers to the countries of East Asia, e.g. China, Japan, Koreas, Hong Kong (China), Taiwan, etc. Such critics usually advise using an alternative term, such as “West Asia”. The official UN designation of the area is “Southwest Asia”. With the disappearance of the Ottoman Turkish Empire in 1918, Near East largely fell out of common use in English, while Middle East came to be applied to the re-emerging countries of the Islamic world. However, the usage of Near East was retained by a variety of academic disciplines, including archaeology and ancient history, where it describes an area identical to the term Middle East, which is not used by these disciplines (see Ancient Near East). So in shorter words, the term Middle East came about when the UK/French part of the world used the term. The Eisenhower Doctrine, a 1957 policy of the United States government, was the first to officially use the term Middle East.[9] Secretary of State, John Foster Dulles defined the Middle East as “the area lying between and including Libya on the west and Pakistan on the east and Turkey on the North and the Arabian peninsula to the south, plus the Sudan and Ethiopia.”[9] In 1958, the State Department explained that the terms “Near East” and “Middle East” were interchangeable, and defined the region as including only Egypt, Syria, Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Qatar.[13] The