Cuba
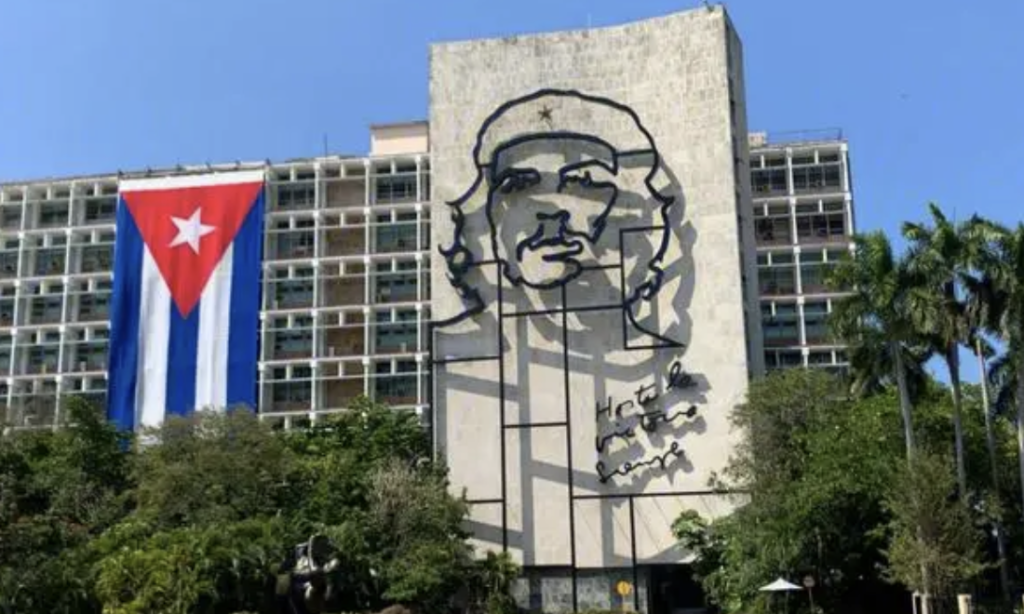
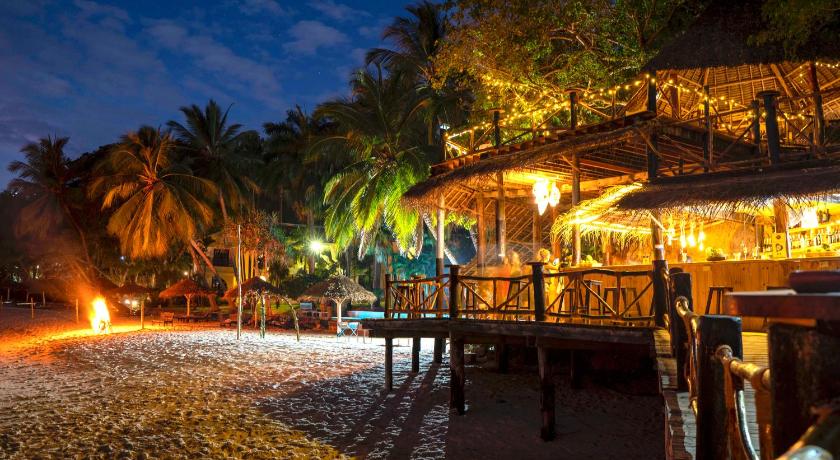
Due to decades of political isolation, Cuba has been largely overlooked by the world. This is a colonial city, and the white beaches here have not been discovered by tourists, so the natural environment of the island is well protected and not polluted by chain enterprises such as McDonald’s and Starbucks. All of this has added to Cuba’s charm, and the locals are really happy to see tourists arrive on this colorful island. Therefore, if you are looking for a real travel experience, this is currently your best travel destination. From French neoclassicism and decorative art to the influence of Spanish Moorish and colonial Baroque styles, Cuban architecture will never disappoint tourists. Whether in Old Havana, which is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, or on the cobblestone streets of Trinidad, you can easily take photos of brightly colored exterior walls. Although buildings like the Capitol and Havana Cathedral are undoubtedly the central stage of Havana, don’t miss out on other less obvious architectural treasures in this city. Havana’s crumbling colonial architecture has its own beauty, all of which adds to its charming charm. Cuba has numerous beaches, approximately 300 of them. Each one is a perfect scene – a pink white beach surrounded by blue seawater. Beautiful beaches such as the Prayalo Flamenco dance on Cayo Coco Island and beach volleyball on Cayo Guillermo Island. But no matter where you choose, you will feel a distance of one million miles from home. Cuba enjoys a warm subtropical climate and is an excellent vacation destination almost at any time of the year, with ample sunshine. The island receives an average of 8 hours of sunshine per day, with approximately 300 sunny days per year. Cuba has only experienced two different seasons in a year, with the dry season lasting from November to April and the rainy season from May to October. Although named the Western Season, these months often see rainstorm pouring down, but it soon dries up, exposing the clear sky again.